With the ever increasing cost of petrol fuels, more and more people are choosing to purchase diesel driven cars. Indeed, manufacturer sales numbers clearly show that most of the car buyers in India prefer to invest more in their car, if it means that they can lock in a lower cost of operating the car.
We have earlier done a thorough analysis on which fuel to choose for your car in which it was shown that diesel engines, even though they come at a higher cost and have higher maintenance costs, save you a significant amount on your fuel costs, since both the mileage and the per litre cost of the fuel is less.
With the increase popularity of diesel cars, today we turn to take a look at the diesel engine in more detail. How does it work? And how should you maintain a diesel car to keep it in tip top shape?
The Working of a Diesel engine
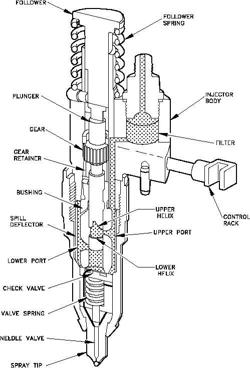
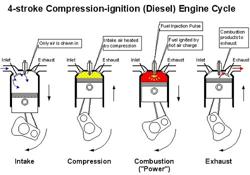
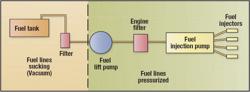
Diesel engines and petrol engines share several similarities. They have a number of components in common such as the crankshaft, pistons, valves, camshaft, and coolant and oil pumps. However, a key difference between the two is that the diesel engine lacks an ignition system. Instead of relying on a spark for ignition (as in petrol engines), a diesel engine uses heat produced by compressing air in the combustion chamber to ignite the fuel. This is done by using a Fuel Injector instead of a spark Plug.
Fuel is supplied to a Fuel injection pump and from there to injectors positioned on each cylinder. Timing and pressure is set to inject a fine spray of diesel at the end of the compression stroke. The heat of compressed air entered into the cylinder then ignites the fuel and thus begins the power stroke.
Fundamentally, using compressed, hot air as well as diesel spray ensures that the air and diesel particles can mix better so that ignition can take place. This is because diesel as a liquid is not easy to ignite.
Glow plugs are used in diesel engines only to warm the combustion chamber when engine is cold. As the above explained, the air in the cylinder needs to be hot to ignite the diesel spray. Hence, cold starting is impossible without these plugs because even the high compression ratios cannot heat cold air enough to cause combustion. Thus when you’re just starting your engine, these glow plugs will warm up the air in the combustion chambers.
Types of Diesel Engines
There are various types of branded diesel engines which are used by different manufacturers. Though they are in essence similar, let's take a look at the various engines that are there.
- CRDi Engine - Common Rail Direct Engines : used by Hyundai, Ford , BMW etc
- TDI Engine - Turbo-charged Direct Injection: initially seen in VW Group cars, turbo diesels are now also used by BMW, among others.
- Multi-jet Fuel injection Engine : Maruti Swift Dzire, Suzuki Swift Diesel, Tata Cars, Fiat cars etc
- Naturally Aspirated
Diesel fuel supply system and maintenance
Maintenance of diesel car is similar to that of petrol car as far as body, interiors, suspension, and steering go. The difference lies in points to be taken care of with respect to engine and fuel supply system, as indeed, that is the only difference between the two.
Knowing more about the Fuel injection system will certainly help to understand why diesel engines are costlier and more complicated as compared to their petrol counterparts, which also explains the more complicated maintenance.
The diesel engine runs on a four stroke fuel cycle. This consists of two major components - air supply and fuel supply
Air is taken during suction stroke and compressed to high pressure and temperature (520 degree to 720 degree centigrade) according to the compression ratio of 12:1 to 20:1. The high temperature of air at end of the stroke is sufficient to ignite fuel.
The fuel is injected into cylinder at end of end of compression stroke. The pressure of fuel injected lies between 100 to 200 bars. During process of injection, fuel is broken into very fine droplets. The droplets vaporize taking heat from hot air and form a combustible mixture and start burning. As burning starts, vaporization of fuel is accelerated as more heat is available. As combustion progresses, amount of oxygen available for burning reduces and therefore heat release is reduced.
Ignition delay is a important term used in diesel engine fuel supply system. It is the period between start of injection and start of ignition. It’s about 0.001 seconds for high speed engines and 0.002 seconds for low speed engines. The whole performance of engine depends upon delay period. The lesser delay period, better is engine performance.
After the ignition, the temperature and pressure rise rapidly and power is created.
Functions of fuel injection system
The main functions of fuel injection systems are as follows:
- Filter the fuel
- Meter or measure correct quantity of fuel to be injected
- Time fuel injection
- Control rate of fuel injection
- Automise or break up the fuel to fine particles
- Properly distribute fuel into combustion chamber
To accomplish these factors, fuel injection systems are manufactured with great accuracy, especially the parts that actually meter and inject fuel. Some of the tolerances between moving parts are very smal, in the order of 1 micron. Such closely fitting parts require special attention during manufacture and hence the injection systems are costly.
Maintenance of fuel injection system is a technical matter and has to be carried out by trained mechanics, so it’s not dealt with in detail. However, some of the focus points for the diesel engine can be mentioned as smoke and its control.
Smoke
In combustion engines, if fuel is burnt at a relative Fuel/Air ratio greater than 1.5, the pressure developed in these engines produce soot. The quantity of soot formed depends upon following factors.
1. The fuel air ratio
2. The fuel type
3. The pressure
The soot thus formed will burn completely provided it has adequate quantity of oxygen to support it. When it doesn’t have sufficient oxygen to support the combustion process, it exits out as exhaust fumes. When more in quantity, the soot that rushes out is visible and forms smoke.
It is to be noted that soot is not carbon. In fact, soot formation during early part of combustion process is common to all diesel engines but it is consumed during later part of combustion.
Many theories have been put forward for formation of smoke but basic reactions leading to formation of smoke are not fully known.
The smoke of diesel engine is generally of two types
- Blue white smoke. It is caused by liquid droplets of lubricating oil or fuel oil while starting from cold.
- Black smoke: Consist of carbon particles suspended in exhaust gas and depend upon air/ fuel ratio. Black smoke increases rapidly with increase in load and when the available air is reduced.
Apart from major factors such as faults in injection system, load on engine, fuel air ratio, engine type and speed, it also depends upon quality of fuel used.
In effect, monitoring your diesel car's smoke output allows you to understand its health.
Maintenance of your diesel car
Maintenance plays a major role in controlling smoke. Good maintenance is a must to get low smoke levels - or vice versa, low smoke levels show good maintenance. Improper maintenance affects the injection characteristics and quantity of lubricating oil which pass across piston rings and thus exercise a significant effect on engine tendency to generate smoke.
Following the scheduled maintenance as mentioned in particular car owner manual is needed to ensure good condition.
Diesel odour and its control
The general complaint with diesel vehicles is about their foul smell or odour. It is due to products of oxidation of fuel in exhaust. The partial oxidation may be because of very lean mixtures of fuel and air such as during idling or due to quenching effect. Factors such as Fuel/air ratio, Engine operation mode, engine type, fuel consumption affect odour production.
Though many manufacturers claim that odour additive compounds can reduce intensity of odour, it has been found in practice that these hardly have any effect.
Periodic Maintenance
- Follow maintenance instructions given in owner’s manual supplied with vehicle
- Always use lubricants of correct grade and quality at correct intervals as specified by manufacturer.
- Replace engine oil in procedure given below.
- Drain out the engine oil while warm.
- Fill in flushing oil up to min (minimum) mark on dip stick and run engine at about 1000 rpm for 10 mins.
- Drain out flushing oil
- Refill with engine oil of specified grade
- Use purest available water for the radiator top up.
- In order to avoid crack of cylinder block, do not top up radiator with cold water after switching off engine when water level is very low and engine is rather hot.
- Radiator cap should be removed slowly. Slight opening will allow pressure to reduce and later can be completely taken out.
- Use only distilled water for top up of battery.
- During parking the vehicle for long durations such as 15 days or for few months etc, disconnect the battery terminal.
- To check condition of oil
- Park car on level surface
- Take out oil dipstick.(it is generally easy to locate, if case can’t you find it then use owner’s manual for the same
- Wipe the dipstick and re-insert till it is closed completely and take out.
- If the oil level is up to the second mark on the dipstick then oil level is correct. It should at least be at minimum level. If it’s below minimum then don’t run the engine.
- Taking few drops of oil rubbing with fingers gives feel of thickness of the oil. It should be very smooth. If thickness is experienced then it indicates contamination. One can also gauge contamination by looking at the oil.
- Reinsert the dipstick and close it properly.
Some of the general points to be considered under periodic maintenance are as below.
Other minor maintenance tips for car
- Replace bulbs periodically with bulbs of same type and capacity
- Avoid parking vehicle under SUN as much as possible especially in summer.
- Avoid spilling of Diesel, alcohol, sodium compounds, windshield solvents or brake fluids on body finish
- Periodically clean water drain holes at bottom of doors to avoid rust formation
- Get antirust coating done for underbody once in a year or two as convenient
- Never wash or polish car in sun especially during summer
- Park the vehicle under cover during nights, rainy days and winter months to avoid excessive condensation of water on vehicle body which would affect its finish.
- Wipeout all drops penetrated inside the body as a result of moisture condensation. Else it will also lead to rust formation
- Dont scuff painted surfaces with any rough object which may create scratches
- Dust off body before washing or wiping with moist cloth
- Polish the vehicle with good quality wax polish after washing
Washing and Cleaning and Greasing of vehicle
- Wash and clean the lower part of vehicle first, including wheels with water jets and sponge.
- Wash the body avoiding excessive pressure water spray. Use a sponge in washing. Rub gently to avoid scratch
- Dry the vehicle with chamois or with cloth which can absorb more water and easy to use
- Remove grease, oil and tar spots from painted parts by wetting with petrol and wiping immediately with a dry cloth
- Cleaning apply small amount of grease to all metal joints such as Door hinge, notches etc
- For cleaning chrome plated parts, apply some natural Vaseline and then rub with soft and clean rag as well as chamois
- Clean window and wind shield with linen cloth or a very soft chamois. Use windshield washer solvent or water containing some alcohol for very dirty glass panes
- Clean rubber mats with soap and water
Clean leather seats or other parts with a wet and soapy sponge or cloth. Rinse carefully with clean water and dry well with chamois
Conclusion
The aim of this article is to create awareness of importance and why maintenance of diesel engines is comparatively costly with respect to petrol engines especially with problems related to fuel supply system. As maintenance schedule for each car varies depending upon specifications and technology used, following owner’s manual and taking care of points mentioned above will certainly help customers to get best of the car performance.
We have dealt with similar tops on working of diesel engines, comparison on petrol/diesel engines, mileage tips etc under our auto guide sections. We hope this article will serve as additional information regarding diesel vehicle maintenance.